is using a volumetric pipette accuracy|volumetric pipette disadvantages : Chinese Using a Volumetric (Transfer) Pipet . A volumetric (Transfer) pipet delivers its marked capacity in one delivery capacity is (printed on the bulb). These pipets are filled to a level above the capacity mark and then water is released until the meniscus is ned with thealig zero graduation. The pipet is then completely emptied into the receiving . Laboratory autoclaves produced by Tuttnauer are trusted by many leading laboratories and research institutions for sterilization and infection control, depending on Tuttnauer’s quality and service with complete peace of mind.We manufacture replacement gaskets for popular brands of tabletop sterilizers. Our products .
{plog:ftitle_list}
IVto the artist:website: http://www.mountain-goats.com/twitter: https://twitter.com/mountain_goatstumblr: https://johndarnielle.tumblr.com/_____Hand me.
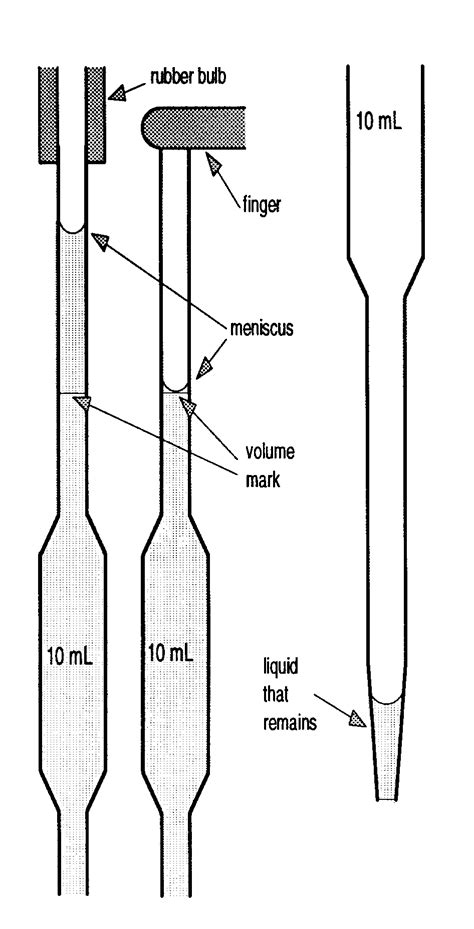
In this course you will use three types of precision calibrated glassware: burets, pipets and flasks. This type of calibrated glassware is usually referred to as volumetric glassware. This precision glassware is capable of measurements of volume that are good to four significant digits and is .You can also measure out smaller volumes precisely and accurately with a volumetric pipette or tiny volumes with a micropipette. Pipettes are sometimes called “transfer pipettes” because .
volumetric pipette technique
Using a Volumetric (Transfer) Pipet . A volumetric (Transfer) pipet delivers its marked capacity in one delivery capacity is (printed on the bulb). These pipets are filled to a level above the capacity mark and then water is released until the meniscus is ned with thealig zero graduation. The pipet is then completely emptied into the receiving . A volumetric pipette is a laboratory instrument used to measure and transfer a specific volume of liquid with a high level of accuracy and precision. It is designed to deliver a single, fixed volume of liquid, often to the nearest hundredth or thousandth of a milliliter. Volumetric pipettes typically consist of a long, narrow glass tube with a bulbous portion near . Designed to draw and dispense a fixed volume of liquid with great accuracy, pipettes play an indispensable role in any laboratory setting. This guide serves to illuminate the process of using a pipette correctly and effectively. . Using a volumetric pipette requires care and understanding. Here is a step-by-step guide to use it properly .If liquid was drained to the bottom of the pipette with a T.C. pipette, use pressure from a pipette bulb to blow out the residual drop. Do not blow out the residual drop when using a T.D. pipette. If a volumetric pipette is used, the liquid should be withdrawn with suction to the marked line above the glass bulb (indicated in Figure 1.25d). The .
This accuracy makes volumetric pipettes indispensable in many scientific disciplines, from chemistry to biology. ALSO READ: What Is The Difference Between Bipolar 1 And 2. Ease of Use. Volumetric pipettes are relatively easy to use. Once the user understands the correct technique, measuring and transferring liquids becomes straightforward.
Labs typically use air displacement pipettes, as they're less expensive and well suited to most liquids, including viscous and volatile liquids – as long as the correct technique and pipette tips are used (see section The influence of the right pipette tip).However, if you regularly need to pipette very viscous or very volatile liquids, a positive displacement pipette might be .Where pipettes are used to accurately and precisely transfer volumes of liquid in the microliter range. Another difference between Burette and Pipette is that the Burettes are larger than pipettes with higher capacity of liquid to dispense. That’s why the accuracy of a burette in releasing small volumes is lesser than a pipette. The use of volumetric pipettes is especially crucial in analytical chemistry, where precise and accurate volume measurements are essential for creating standard solutions, preparing samples, and conducting titrations. The ability to measure volumes with such accuracy allows researchers and analysts to obtain reliable and reproducible results. Additionally, if the solution is not carefully prepared and well-characterized, using an accurate volumetric pipette will not compensate. Once the volumetric pipette is filled, it is imperative there are no entrapped air bubbles or detritus. At the top marking, the liquid will form a curve, since gravity pulls downward on the liquid most .
Example: The pipette volume is set at 20 µl. Accurate, but not precise: The mean volume is the correct (set) volume, but the separate pipettings differ from the set volume. . Factors Affecting Pipette Accuracy Temperature. Temperature has many effects on pipetting accuracy. The factor that has the greatest effect is the temperature . The proper use of a pipet is a skill that takes time and practice. Try at least three practice runs of filling the pipet and delivering the water back to the 250 mL beaker. For the glassware listed below, the glassware will be used to transfer water to a beaker for weighing. 50 mL buret ; 10 mL volumetric or graduated pipet
We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. The faithful pipette you use every day? Check it every three months. The beloved but not used so often pipette? An annual check should suffice. How to Check the Accuracy of Your Pipette: The Weight of Water. The most common way to check your pipette accuracy is by weighing water. The density of water is 1 g/mL. Burettes are the most accurate way of measuring a variable volume of liquid between 0 cm 3 and 50 cm 3. They are most commonly used in titrations. Careful: Read the burette scale from top to bottom as 0.00 cm 3 is at the top of the column Volumetric pipettes are the most accurate way of measuring a fixed volume of liquid,. They have a scratch mark on the .
displacement single-channel pipettes are the most used laboratory instruments. The same pipette can be used for multiple applications. Multichannel pipettes are most commonly used in microplate applications, such as ELISA, PCR, or cell culture. Manual multichannel pipettes offer instant usability for small scale multichannel work. Volumetric Pipettes. Volume pipettes allow for the measurement of a solution with a particularly high level of accuracy. Typically featuring a large bulb complete with a narrow long portion and single graduation mark, they are calibrated for a specific volume. Their highly accurate measurements are usually present in ml (millilitres). Graduated . Consequently, the volume range of a pipette can significantly impact accuracy and precision. Essentially, the closer the dispense volume is to the total volume of the pipette , the better the . To deliver the desired volume hold the pipet in a vertical position, and drain the solution into the container with the tip of the pipet touching an inner wall of the container. . have been calibrated with high precision and accuracy in order to quickly and easily transfer specific volumes of solution. The more common micropipette has the .
It’s important to remember that using Mohr pipettes correctly is essential to ensuring precise measurements. This entails letting the liquid drain entirely and taking an accurate reading of the volume at the meniscus. Consistent calibration and upkeep are also required to guarantee the pipette’s accuracy throughout time. The main difference between a graduated pipette and a volumetric pipette is that graduated pipettes have multiple graduation marks to measure various fluid volumes, while volumetric pipettes have only one graduation mark to measure a single specific volume. Volumetric pipettes deliver fixed volumes with high accuracy, essential for precise lab .The pipette is checked at the maximum volume (nominal volume) and at the minimum volume or 10% of the maximum volume, whichever is higher. A series of ten pipettings is performed with both volumes. Calculate the accuracy and precision using the Formulas section below.The volumetric measurement of liquids is a routine operation in the laboratory. Therefore, volumetric instruments, such as volumetric flasks, bulb pipettes, graduated pipettes, graduated cylinders and burettes are standard equipment. They can be made from glass or plastic. Sup-pliers offer volumetric instruments in varying qualities.
It is called volumetric pipette to a specific type of pipette for the most accurate and precise measurement of liquids in a laboratory. A pipette is nothing more than a transparent borosilicate glass cylinder, which is an element that is easy to clean, chemically an inert material and undergoes little deformation. . For example, if you use a .
The main attribute of volumetric pipettes is their high accuracy and precision. They are manufactured and calibrated to deliver a specific volume of liquid at a specific temperature, usually 20°C. This calibration ensures that the delivered volume is highly accurate, making volumetric pipettes suitable for critical applications where precise . Technique E: Volumetric Transfer of Reagent Using Pipet . Section 1: Purpose of Technique . This technique describes how to properly use a volumetric pipet to collect, measure, and transfer a precise volume of liquid. Section 2: Operations for Volumetric Pipet Transfer . One of the most common type of volumetric glassware is the volumetric pipet.
Graduated cylinders, volumetric flasks, bulb pipettes, graduated pipettes, and burettes are volumetric instruments. They are calibrated; however, like any other measuring instrument, they only have a limited accuracy and precision. The accuracy and precision do not only depend on the type of the instrument (e.g. graduated cylinder or pipette). Volumetric pipettes are more accurate than graduated pipettes and burettes because they are designed to deliver a fixed volume of liquid with high precision. In the laboratory, precise measurement and transfer of liquids are essential for accurate experimental results. Two common tools for this purpose are the burette and the pipette.
volumetric pipette how to use
how to determine the specific gravity with refractometer
volumetric pipette drawing with label
Black Silicone door seal for Ritter-Castle 999 Compare Out of stock
is using a volumetric pipette accuracy|volumetric pipette disadvantages